Prompt Engineering Fundamentals
Essentials of Prompt Engineering
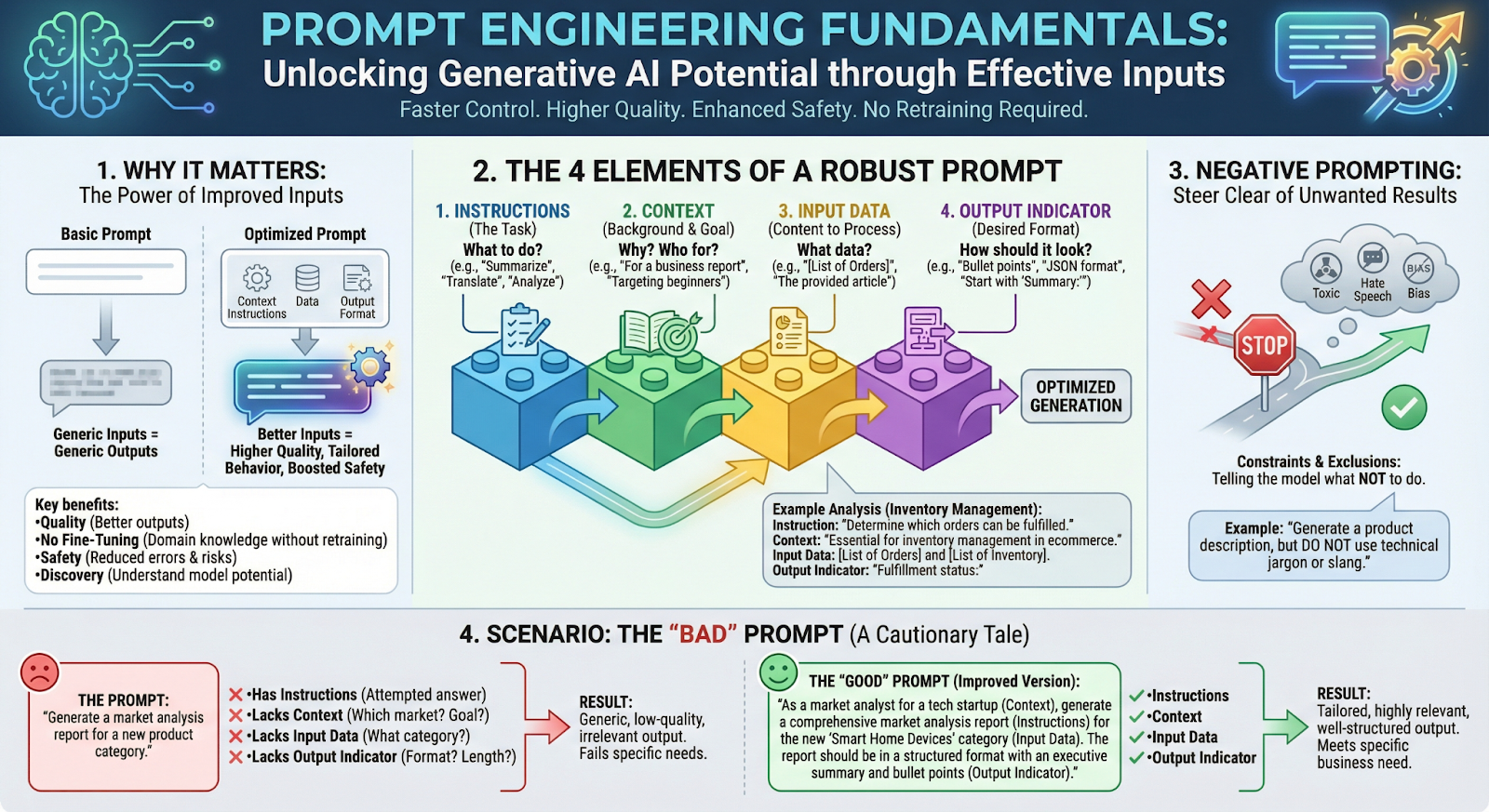
Section titled “Essentials of Prompt Engineering”Improving how we prompt a Foundation Model (FM) is the fastest way to control Generative AI. By adjusting our inputs (questions/instructions), we can change the behavior of the model without needing to retrain it.
Key Benefits
Section titled “Key Benefits”- Quality: Better inputs lead to higher-quality outputs.
- No Fine-Tuning Needed: You can equip the model with domain-specific knowledge or tools without touching the model parameters.
- Safety: Good prompts can bolster safety measures and reduce errors.
- Discovery: It helps us fully understand the potential of the model.
The CLEAR Framework
Section titled “The CLEAR Framework”A helpful mnemonic for crafting effective prompts comes from “The CLEAR Path: A Framework for Enhancing Information Literacy through Prompt Engineering” by Leo S. Lo. The framework outlines five principles:
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Concise | Strip unnecessary words and focus on essential information. |
| Logical | Structure prompts with clear flow and natural progression. |
| Explicit | Specify exact output format, scope, and content requirements. |
| Adaptive | Iterate and refine prompts based on AI responses. |
| Reflective | Continuously evaluate outputs for accuracy and relevance. |
CLEAR in Practice
Section titled “CLEAR in Practice”| Principle | Instead of… | Try… |
|---|---|---|
| Concise | ”Can you provide me with a detailed explanation of how REST APIs work?" | "Explain REST APIs and their core principles” |
| Logical | Random, unstructured requests | ”List the steps to deploy a Node.js app, from setup to production” |
| Explicit | ”Tell me about Docker" | "Provide a concise overview of Docker, covering containers, images, and basic commands” |
| Adaptive | Accepting vague results | If “Discuss cloud computing” yields generic output, try “Compare AWS Lambda vs Azure Functions for serverless backends” |
| Reflective | Moving on without evaluation | After receiving content, assess quality and adjust subsequent prompts |
The framework was designed to help develop critical thinking skills for evaluating and creating AI-generated content—a skill valuable for developers and non-developers alike.
The 4 Elements of a Prompt
Section titled “The 4 Elements of a Prompt”A robust prompt typically contains four specific components. Including all of them drastically improves results.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Instructions | The specific task description. What do you want the model to do? |
| Context | External information or background. Why are we doing this? Who is it for? |
| Input Data | The content that needs to be processed. What data are we analyzing? |
| Output Indicator | The desired format. How do you want the answer to look? |
Example: API Error Log Analysis
Section titled “Example: API Error Log Analysis”- Instruction: “Given a list of API error logs, categorize each error by severity level.”
- Context: “This task helps the DevOps team prioritize bug fixes for a web application.”
- Input Data:
[List of Error Logs]with timestamps and error codes - Output Indicator: “Error Category:” (Signals the start of the response)
Negative Prompting
Section titled “Negative Prompting”Sometimes it is easier to tell the model what not to do than to explain what it should do.
- Definition: Providing constraints or examples of what should be excluded.
- Goal: To steer the model away from unwanted behaviors, toxic content, hate speech, or bias.
- Example: “Write a README for this Python library, but do not include installation steps or license information.”
Scenario: The “Bad” Prompt
Section titled “Scenario: The “Bad” Prompt”The Prompt: “Generate documentation for my API.”
Why it fails:
Section titled “Why it fails:”| Element | Status |
|---|---|
| Instructions | ✅ Present — the model will try to answer |
| Context | ❌ Missing — What kind of API? Who is the audience? |
| Input Data | ❌ Missing — What endpoints? What parameters? |
| Output Indicator | ❌ Missing — Format? Structure? |
Result: The output will be generic, low-quality, and likely irrelevant to your specific API.
Modifying Prompts for Better AI Outputs
Section titled “Modifying Prompts for Better AI Outputs”While Foundation Models (FMs) are capable, their output quality relies heavily on the prompt. Modifying prompts and adjusting inference parameters allows you to unlock the full potential of the model without fine-tuning.
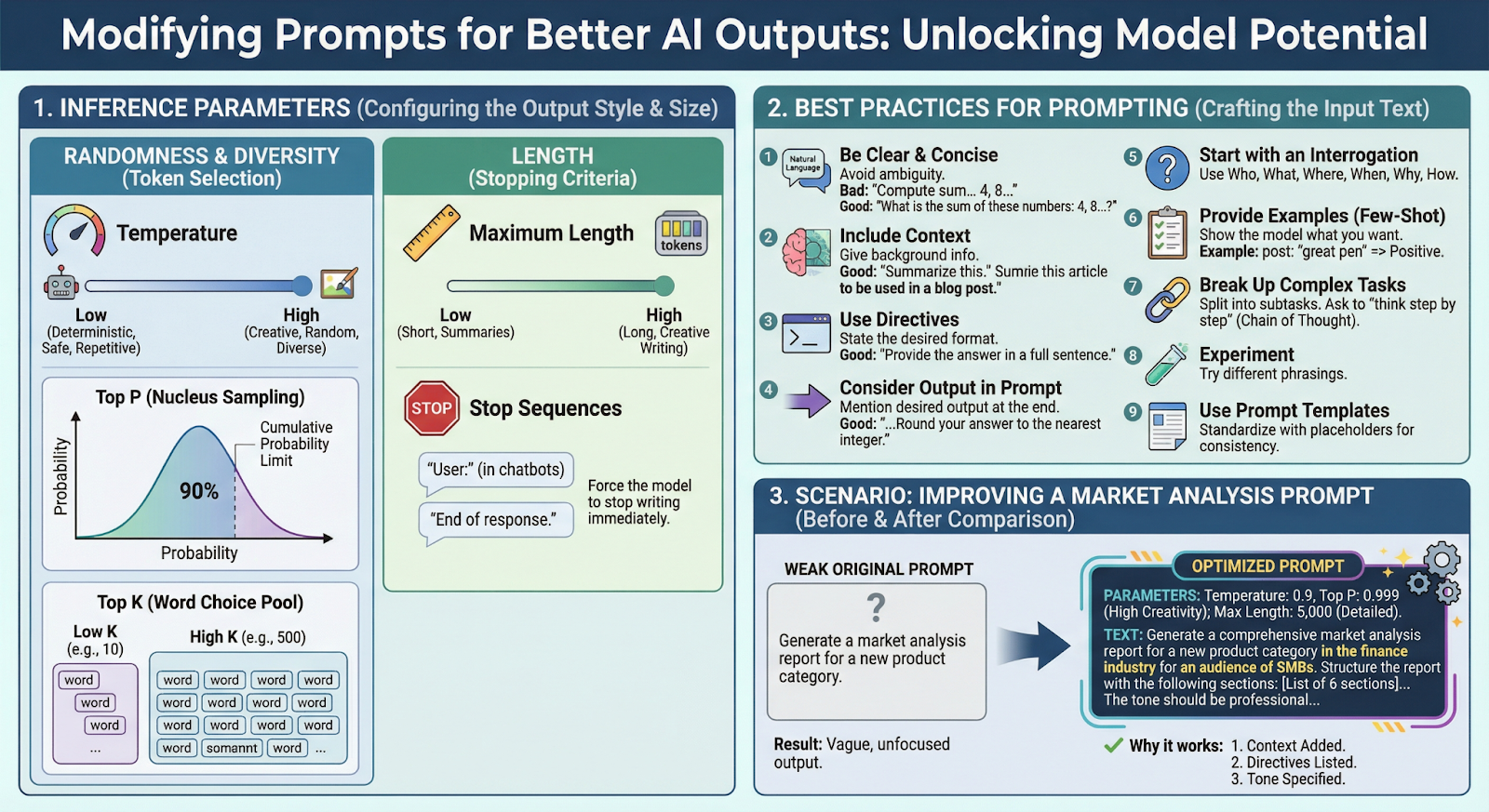
Inference Parameters
Section titled “Inference Parameters”These are settings you configure before sending the prompt. They control the “style” of the response (Randomness/Diversity) and the “size” of the response (Length).
A. Randomness and Diversity
Section titled “A. Randomness and Diversity”These parameters change how the model selects the next word (token).
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Controls the “creativity” of the model. Low = deterministic, safe. High = creative, diverse. |
| Top P (Nucleus Sampling) | Limits word choices to a cumulative probability (e.g., top 90%). |
| Top K | Limits the choice to the top K most probable words. Low (10) = focused. High (500) = diverse. |
B. Length
Section titled “B. Length”Controls when the model stops writing.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum Length | The hard limit on tokens generated. Set low for summaries, high for detailed docs. |
| Stop Sequences | Special words/symbols that force the model to stop immediately. |
Example: In a coding assistant, "```" might be a stop sequence so the AI stops after completing a code block.
Best Practices for Prompting
Section titled “Best Practices for Prompting”Beyond parameters, the actual text of the prompt matters most.
Key Guidelines
Section titled “Key Guidelines”| Guideline | Bad Example | Good Example |
|---|---|---|
| Be Clear and Concise | ”Parse data… JSON…" | "Convert this CSV file to JSON format.” |
| Include Context | ”Debug this code." | "Debug this Python function that handles user authentication.” |
| Use Directives | — | “Provide the response as a numbered list.” |
| Consider Output in Prompt | — | ”…Return only the function name, nothing else.” |
More Tips
Section titled “More Tips”- Start with an Interrogation: Use Who, What, Where, When, Why, How.
- Provide Examples (Few-Shot Prompting): Show the model what you want.
- Example:
input: "bug fixed" => commit_type: fix
- Example:
- Break Up Complex Tasks: Split into subtasks. Ask the model to “think step by step” (Chain of Thought).
- Experiment: Try different phrasings.
- Use Prompt Templates: Standardize your prompts with placeholders for consistency.
Scenario: Improving a Technical Documentation Prompt
Section titled “Scenario: Improving a Technical Documentation Prompt”The Weak Original Prompt
Section titled “The Weak Original Prompt”“Generate documentation for my REST API.”
The Optimized Prompt
Section titled “The Optimized Prompt”Parameters:
- Temperature (0.3): Low setting for consistent, accurate output
- Max Length (3,000): Allows for detailed documentation
The Text:
“Generate comprehensive API documentation for a REST API that handles user authentication. The audience is frontend developers integrating with this API. Structure the documentation with: Overview, Authentication Flow, Endpoints List, Request/Response Examples, Error Codes, and Rate Limits. Use a professional, developer-friendly tone.”
Why it works:
Section titled “Why it works:”| Improvement | What was added |
|---|---|
| Context | ”REST API for user authentication” + “Frontend developers” audience |
| Directives | Explicitly listed the 6 sections required |
| Tone | Specified “Professional, developer-friendly” |